-
Resistance:
The resistance (R) of a circuit element is defined as the ratio of the
potential
difference (V) across the element to the current (I) passing through
the
element,
R = V/I
The units of resistance are Ohms 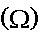
1 Ohm = 1 Volt/Ampere
- Ohm
's Law:

The resistance of a circuit element is always defined by
the
above relationship (R=V/I). If the value of the resistance for a
particular
circuit element is constant, independent of the current (and voltage)
the
element is said to obey
Ohm's Law
. Note that this means that the electric current through the
element
is directly proportional to the voltage.
Metallic conductors satisfy Ohm's Law.

- Power:
We have already seen that the work done raising a charge Q through a
potential
V is given by, W = QV. Using the fact that Q = It and W/t = Power
Power = I V
(Watts = Amps x Volts)
Using the definition of resistance we find
Power = I V = I2 R = V2/R
The power is the rate at which energy is dissipated in a
(resistive) current element, usually in the form of heat.


![]()


