
p = mv
Units: kg.m/s (SI); slug.ft/s (British)
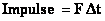
Units: N.s (SI); lb.s (British)
Impulse = Momentum change
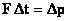
or
Force = Rate of change of momentum
Important basic principle of Science
![]() "Total momentum of a system remains constant,
"Total momentum of a system remains constant,![]()
when the net external force acting on the system is zero"
![]() Within
the system objects may collide with each other, thus exerting
forces on each other. However, Newton's 3rd law states that these
forces are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction, therefore
there
is no net force. The system conserves
momentum.
In order to ensure momentum conservation we must choose our "system"
such
that the net force is zero, in which case;
Within
the system objects may collide with each other, thus exerting
forces on each other. However, Newton's 3rd law states that these
forces are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction, therefore
there
is no net force. The system conserves
momentum.
In order to ensure momentum conservation we must choose our "system"
such
that the net force is zero, in which case;
"Total momentum of system before collision = Total momentum
of system after collision"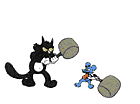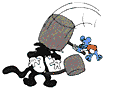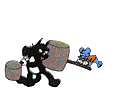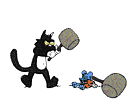
Note that since momentum is a vector quantity, this equation is
actually three scalar equations, one for mometum along each of the
three cartesian axes, x,y,z.
Dr. C. L. Davis
Physics Department
University of Louisville
email: c.l.davis@louisville.edu
