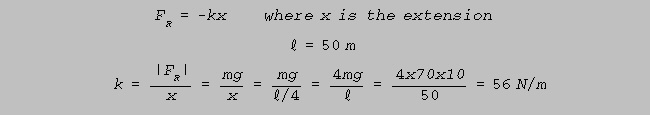
(b) Use the principle of energy conservation to determine how far the "BUNGER" will fall
when jumping from a bridge. (Ignore air resistance) (11)
When suspended
from
a bungee cord, at rest, a 70 kg person - the "BUNGER" - increases
the
length
of a 50 m cord by 25%.
(a) Assuming the cord obeys Hooke's Law, calculate its spring constant. (g = 10 m/s2)
(5)
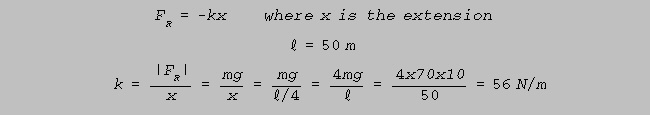
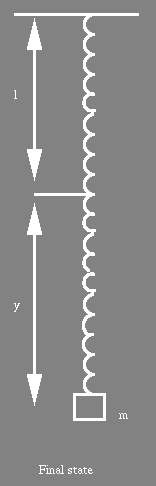
(b) Use the principle of energy conservation
to determine how far the "BUNGER" will fall
when
jumping
from a bridge. (Ignore air resistance)
(11)
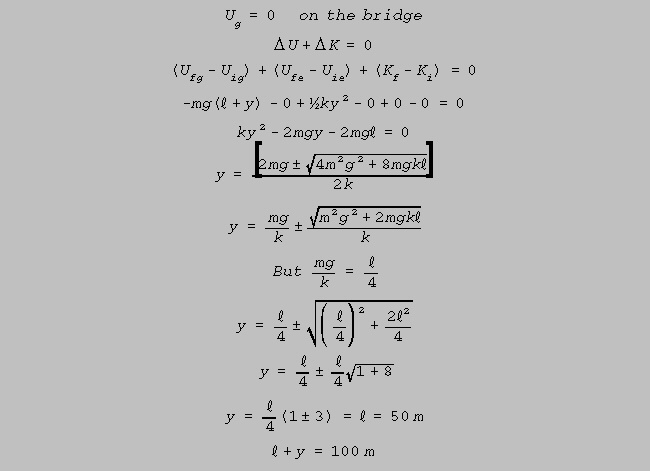
(c) Assuming zero air
resistance
how far would you expect the "BUNGER" to bounce back
towards
the
bridge ?
(2)
Energy is conserved, therefore the bounce would take the "BUNGER" back to the bridge.
(d) In a real situation, on
the
first bounce, the "BUNGER" returns to 10 m below the bridge.
How
much
work is done against the resistive forces from the time the jump
begins
till the
top
of
this first bounce ?
(7)
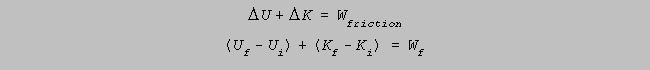
With
initial situation prior to jump and final situation at top of
bounce
then,
![]()
no elastic
PE stored, then