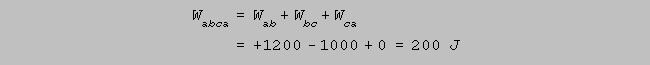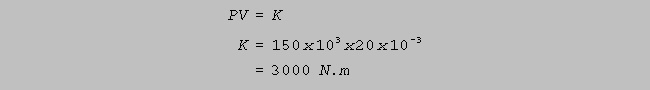
(b) The gas undergoes an isothermal expansion, as indicated below, a to b. How much work is
done by the gas during this expansion ? [ln(1.5) = 0.4] (8)
4) At
constant
temperature, an ideal gas obeys Boyle's Law: PV = K, where K is a
constant.
A
certain
mass of ideal gas has a pressure of 150 kPa when its volume is 20
litres.
(1 litre =
10-3
m3).
(a) Determine the value of the constant K. (4)
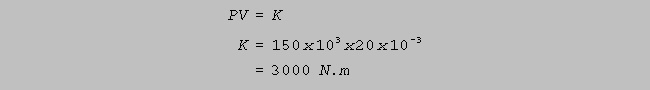
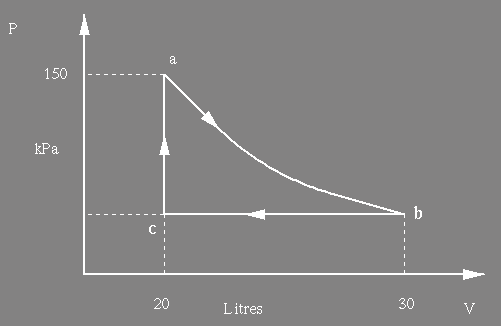
(b) The gas undergoes an isothermal
expansion, as indicated below, a to b. How much work is
done
by the gas during this expansion ? [ln(1.5) = 0.4]
(8)
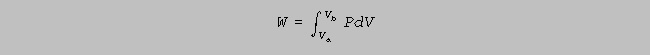
Isothermal
expansion means that T is constant, therefore,
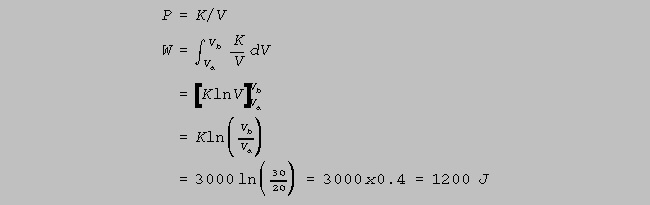
(c) If Ua =
30 J, assuming no change of state from a to b, what is Ub,
and
why ?
(2)
Isothermal expansion Ua = Ub (no temperature change). Ub = 30 J
(d) How much heat enters or leaves the system during the process a to b, and why ? (3)
1st law of thermodynamics
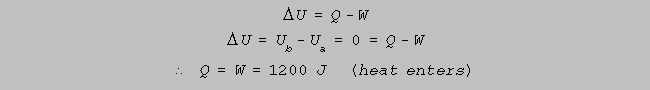
(e) 1000 J of work are
done on the gas to take it from b to a via c. What is the pressure of
the
gas
at
c ?
(4)
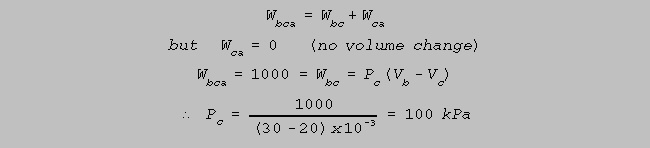
(f) How much work is done
by the gas during the complete cycle abca ?
(4)