3. A ball moves at a constant speed of 2 m/s on a horizontal plane following the path AOBCDEOF, where BCDE is a circular arc. The radius of the circular part of the path is 4 m.
Use the gross approximation pi = 3 throughout this problem.
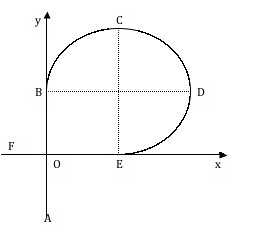
(a) Calculate the distance
traveled by the ball along the round trip OBCDEO. (2)
(¾)2pr +2r = (3x2x3x4)/4 + 2x4 = 18 + 8 = 26 m
(b) How long does it take the ball
to complete this round trip ? (3)
t = d/v = 26/2 = 13 s
(c) Evaluate the magnitude
of the instantaneous acceleration felt by the ball at C. On the diagram, clearly indicate the
direction of the instantaneous acceleration at C. (5)
ac = v2/r = (2x2)/4 = 1 m/s2
Direction towards the centre of the circle
(d) Write the instantaneous
velocity at B in unit vector form. (2)
v = 2 j m/s
(e) Obtain the average
acceleration vector in unit vector form between points B and D. (5)
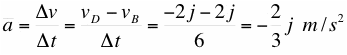
where
![]()
(f) Obtain the average velocity
vector in unit vector form between B and E. (5)
![]()
where
![]()
(g) Calculate the average velocity
over the round trip OBCDEO. (3)
For round trip change in displacement is zero. Therefore average velocity is zero.