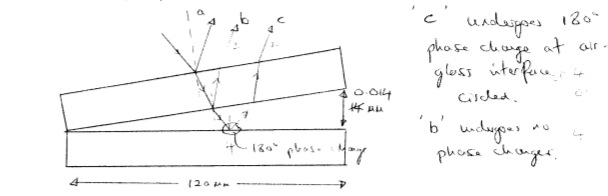
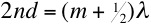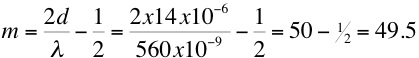4)
A
broad beam of light of wavelength 560 nm is sent directly downward
through the
top plate of a pair of glass plates.
The plates are 120 mm long, touch at the left end and are
separated by a
wire of diameter 0.014 mm at the right end. The
air
between
the
plates
acts
as a thin film.
(a)
Sketch
the path of at least two rays which you would expect to be involved in
thin
film interference.
(4)
"b" and "c" are
representative rays
(b) Why
would
you
expect
a
light
ray
reflected from the top surface of the top plate
not to be involved in this thin film interference ?
(3)
Thickness of
glass plate is much greater than the "air film", which means the thin
film approximation is not valid.
(c)
For
the two rays in part (a) clearly indicate which ray undergoes a 180o
phase change on reflection and at which interface this phase change
occurs.
(4)
"c"
undergoes
a 1800 phase change at the air-glass
interface circled above.
"b" undergoes no phase changes
(d)
Taking
into account any such phase changes write down the condition for a thin
film
interference maximum in terms of the wavelength of the incident light (8), the
thickness of the film (d) and the refractive index of the film (n).
(6)
(e)
Use
this expression to determine the number of bright fringes seen by an
observer
looking down through the top plate.
(8)
n
= 1 (air film)
Therefore, 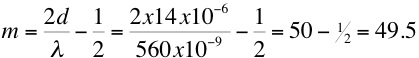 49 bright fringes (at maximum
width of film there is a dark fringe)
49 bright fringes (at maximum
width of film there is a dark fringe)