(a) In which direction is this wave moving ? (2)
1) A traveling wave on a string is described by,
![]()
(a) In which direction
is this wave moving
? (2)
(b) What is the amplitude of
the
wave
? (2)
(c) What is the
wavelength
of the wave
? (3)
(d) What is the frequency of
the
wave ?
(3)
(e) What is the velocity of the wave ? (3)
(f) If 1 metre of the string
weighs
2 N, calculate the tension the string must be under to sustain
the
wave.
(g = 10 m/s2).
(6)
(g) What is the maximum speed of a
particle
on the string ?
(6)
Solution
(a) Calculate the thermal conductivity of the glass (5)
(b) The thermal conductivity
of
air is 40 times smaller than that of glass. The window pane is
replaced
by
a double-glazed pane having a 1 mm air gap, indicated below. What
are
the
temperatures
of
the inner faces of the glass (T1, T2) ?
(10)
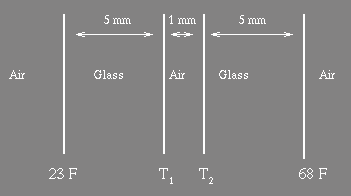
(c) Determine the rate of heat loss through this, double-glazed, window. (6)
(d) In practice a
double-glazed
window is never able to achieve the reduction in heat loss
determined
from
(a) to (c) above. Can you explain why this is the case ?
(4)
(a) Determine the value of the constant K. (4)
(b) The gas undergoes an isothermal
expansion, as indicated below, a to b. How much work is
done
by
the gas during this expansion ? [ln(1.5) = 0.4]
(8)
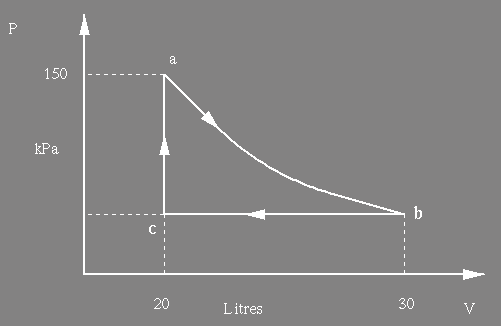
(c) If Ua = 30 J, assuming no change of state from a to b, what is Ub, and why ? (2)
(d) How much heat enters or leaves the system during the process a to b, and why ? (3)
(e) 1000 J of work are done
on
the gas to take it from b to a via c. What is the pressure of the
gas
at
c ?
(4)
(f) How much work is done by the gas during the complete cycle abca ? (4)